What is Fibre to the X (FTTx)?
30 Jul 2024
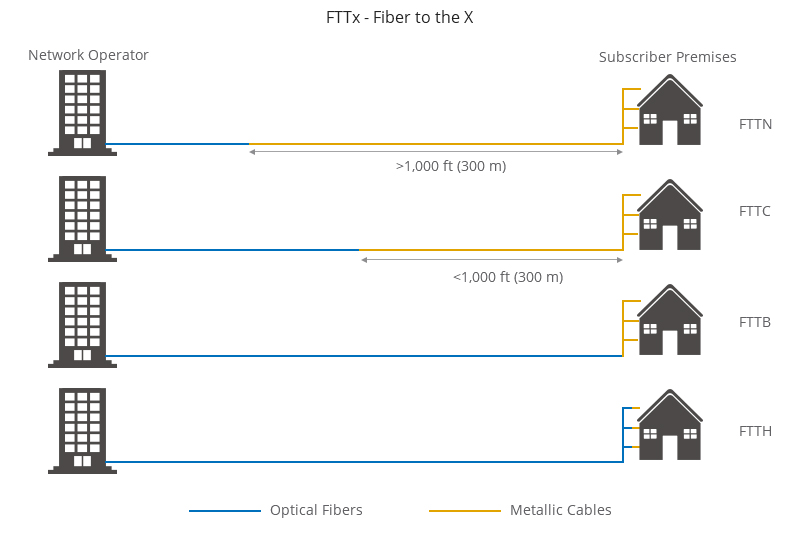
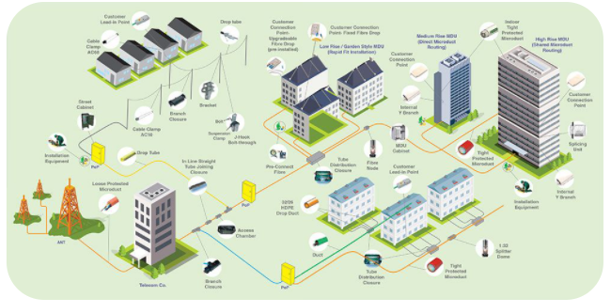
Fibre to the X is a collective term that is used to describe various types of broadband network architectures, depending on wherever they terminate. The ‘X’ in ‘FTTx’ represents a particular object. It could be a home, a cabinet or any end-user premise. Resultantly, FTTx could be Fibre to the Home (FTTH), Fibre to the Building (FTTB), Fibre to the Premises (FTTP) and Fibre to the Curb (FTTC). FTTx is used to drive next-generation access by a significant upgrade to the broadband available by making a step-change in the speed and quality of the service. Fibre to the X (FTTx) network architecture finds its use in Last-mile connectivity. The network is spread out from the end-user premise to the carrier network edge. It can deliver faster and better connectivity to homes and enterprises around the world. FTTx has many benefits related to speed and capacity and that is the reason legacy copper-based networks are being replaced with Fibre to the X (FTTx). Other advantages include higher transmission rates and lower energy consumption. Fibre to the X network takes fibre closer to the end-user. This helps in leveraging the latest construction, connection and transmission techniques. With the development of cloud computing, smart cities and 5G, requirements for higher bandwidth and network speed have increased. Fibre to the X offers a low-latency, high-bandwidth fibre network that can fulfil all these requirements. In addition, it also helps in achieving high capacity and consistent connectivity. It also helps in providing long-distance signal transmission, a lightweight form factor, and immunity against electromagnetic interference.